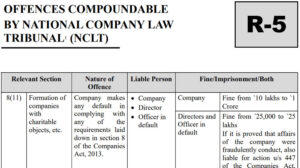
Notwithstanding anything contained in the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973, (Bhartiya Nagrik Suraksha Sahinta, 2023), any offence punishable under this Act, whether committed by a company or any officer thereof, not being an offence punishable with imprisonment only, or punishable with imprisonment and also with fine, may, either before or after the institution of any prosecution, be compounded by (a) the Tribunal; (b) punishable with imprisonment or with fine, and (c) where the amount of fine which may be imposed for such offence exceed Rs. 25 lakhs {Section 441(1) of the Act} provided that any offence covered under section 441(1) shall not be compoundable if the investigation against such company has been initiated or is pending under the Act {Section 441(6) and third proviso to section 441(1) of the Act}.
The applicant before filing of application for compounding offence shall ensure that the alleged offence for which compounding application shall be filed is compoundable under the Act, as offences punishable with imprisonment only, or punishable with imprisonment and also with fine, shall not be compoundable and the offence can be compounded either before or after institution of any proceeding under the Act.The applicant has to also ensure that the maximum amount of fine that can be imposed for violation of concerned offence shall be exceeding `25 Lakhs {Section 441(1) of the Act} and the same offence shall not be compoundable within a period of 3 years from the last date of which similar offence was compounded either by National Company Law Tribunal or Regional Director is not compoundable {Section 441(2) of the Act} and the default for which an application for compounding shall be filed has been made good before filing of said application.
The details provisions can be studied from my book titled as Company Law Procedures and Compliances.